Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM

LG has conducted a survey and reported that more than 90% of people will be anxious because their mobile phones are not inductive, 41% of people will miss important calls when their mobile phones are low, and 17% of men are prone to not having mobile phones. Loss of appointment due to electricity-this phenomenon is called “low battery anxiety disorder”.
As mobile phones carry more and more important functions, it has become a big problem that mobile phones cannot be used without electricity. While taking into account the lightness and thinness of mobile phones, to alleviate the “low battery anxiety” of modern people, we can only increase the charging speed of mobile phones as much as possible-“fast charging” (referred to as “fast charging”) technology came into being.

How can I charge my mobile phone faster?
What is the principle of mobile phone charging?
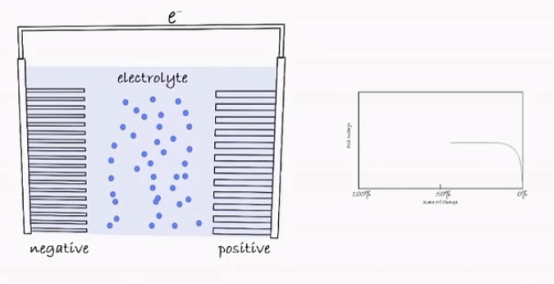
In 1991, Sony and Asahi Kasei jointly released the first commercial lithium battery. Since then, lithium batteries have been widely used in digital 3C products, and mobile phones are no exception. Lithium batteries are divided into a positive electrode and a negative electrode. The positive electrode is a lithium compound, and the negative electrode mainly uses graphite materials, all of which are immersed in the electrolyte.
Whether it is discharging or charging, it is actually a process in which lithium ions move between the positive and negative electrodes of the battery and convert between electrical energy and chemical energy. When charging, due to the action of the electric field, lithium ions move from the positive electrode to the negative electrode and store energy; when discharging, the lithium ions move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode under the action of a chemical reaction, and current power is formed at this time.
The charging speed of a lithium battery is actually the rate at which electrical energy is converted into chemical energy, which is the so-called “power” (P). A brief review of middle school physics, as we all know:
P=IU
Power = current * voltage
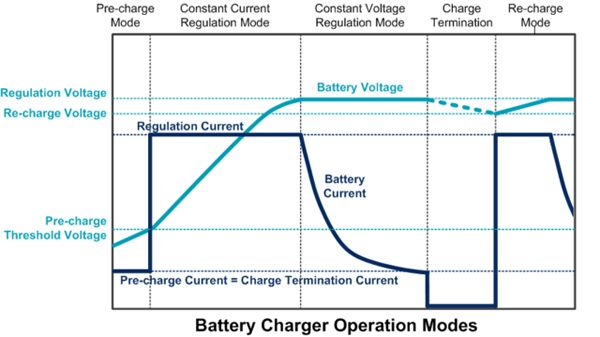
The greater the current or voltage, the greater the power, and the charging speed of lithium batteries should be faster. However, due to the limitation of the lithium battery itself, charging under the condition of undervoltage or overvoltage will cause damage to the battery. Therefore, the charging method of the lithium battery is relatively special, which is usually divided into three stages:
Constant Current Pre-charge Mode
Constant Current Regulation Mode
Constant Voltage Regulation Mode
When the mobile phone is completely out of power, the charger first charges the lithium battery through a constant current with a small current, so that it slowly recovers its activity; after a period of time, the charger will increase the constant current and gradually increase the voltage, which is lithium The main stage of battery charging; when the battery power is about 80%, the charger will slowly reduce the current input under a constant voltage until the current is below a certain critical value, at which time the mobile phone displays fully charged.
Such a charging process is generally controlled by the power management chip built into the mobile phone, and the charger is only regulated according to the instructions of the power chip in most cases.
Therefore, if you want to increase the charging speed of mobile phone lithium batteries, technicians must work hard in the “large current constant current charging” stage.
Before we used mobile phones only to consider functions. In that era, mobile phones did not require high battery capacity and lithium battery technology was not so mature. In order to stabilize lithium battery charging, most manufacturers at that time followed the low rate charging recommended by the state. Standard “5V 0.2C”-that is, the charging voltage is 5V, and the charging current is 0.2C (C represents the rate of battery charging and discharging. When the battery is charged at 1C, it can be fully charged in 1 hour. If it is 1000mAh capacity For a battery, 1C refers to a charging current of 1A; a battery with a capacity of 2000mAh, 1C refers to a charging current of 2A, and so on).
However, with the advent of the era of smart phones, the demand for electric power of mobile phones has greatly increased, and low-rate charging standards have been difficult to meet the demand for charging. At this time, lithium battery technology has also made great progress, with better stability, and improved charging and discharging tolerance, and “fast charging” has begun to take the stage.

What is “quick charge”?
In essence, “fast charging” is a technology that increases the charging power of a mobile phone within a reasonable range, and aims to quickly replenish most of the power of the mobile phone. Since the power is related to the voltage and current, the current “fast charge” is mainly divided into the following two solutions:
High voltage and small current
Low voltage and high current
“Quick charge” is a complete set of charging solutions that require the coordination of the built-in power management chip, charging cable, and charger of the mobile phone, and none of them are indispensable.
As early as 2013, Qualcomm realized the importance of “fast charging” for smartphones. At that time, it launched the Quick Charge 1.0 standard, which improved the charging efficiency by increasing the input current, allowing mobile phones equipped with Snapdragon 600 processors to support “5V 2A” charging.
However, due to the limitation of the micro USB interface, a current exceeding 2A is likely to cause damage, so Qualcomm thought of another solution-increasing the voltage of the interface. In the case of limiting the input current to less than 2A, by increasing the supply voltage, the effect of increasing power can also be achieved.
After continuous improvement, Qualcomm’s Quick Charge 2.0/3.0 can achieve “9V 2A”, which means charging with a maximum power of 18W.
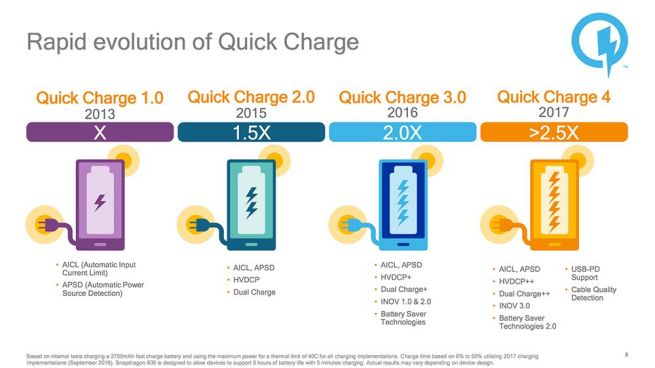
The “high voltage and low current” fast charging solution has inspired many peers. MediaTek’s Pump Express Plus 1.0/2.0, Samsung’s Fast Charge, and Meizu’s mCharge 3.0 are all similar solutions.
However, after the high voltage is input to the mobile phone, there will be a step-down process. At this time, heat loss will occur inside the mobile phone, resulting in serious heat generation. Therefore, many mobile phones using this solution will not activate fast charging when the screen is on to prevent the body from overheating.
In addition, due to the competitive relationship between manufacturers, although the implementation principles of fast charging are similar, there are compatibility issues between each other. Therefore, to improve the charging efficiency, the first thing to do is to choose a compatible charger.
In 2014, OPPO Find 7 equipped with VOOC flash charging was born, and the charging power reached an astonishing 22W. With the hot sale of OPPO mobile phones, the ad slogan “Charge for five minutes and talk for two hours” has also become popular, and consumers have begun to realize the meaning of “fast charging”.
The fast charging principle of VOOC flash charging is the “low voltage and high current” strategy.
Since the micro USB interface limits the size of the input current, OPPO simply customized the entire charging system-the charger, the charging cable, and the internal circuit of the mobile phone, and adopted the battery multi-line charging method, so that the VOOC flash memory can be used ” 5V 4A” for charging.
The advantage of VOOC flash memory is that the heating components during the charging process are basically set in the charger, so that the mobile phone will not overheat while realizing fast charging. But the shortcomings are also obvious. First, it can only be used with VOOC flash charger and charging cable. Second, the cost of the whole solution is relatively high. The price of mobile phones equipped with VOOC flash charging will not be too cheap.
In the final analysis, the crux of the fast charging of mobile phones is the small micro USB interface—you may have noticed that in recent years, more and more mobile phones equipped with USB-C interface (full name USB Type-C) have actually been The precursor of the mobile phone interface revolution. USB-C can be said to be an intersection of future interface standards. It has the following important characteristics:
Support positive and negative plug
Compatible with USB 3.1 standard, the fastest support 10Gbit/s transmission
Supports USB Power Delivery charging protocol, can provide up to 100W of power, and can be two-way power supply
Support DisplayPort, can output audio and video

At present, the most typical application of USB-C is actually on the new host Switch that Nintendo sold at the beginning of the year. Only relying on the USB-C interface, the Switch realizes the functions of positive and negative plugging, host power supply, game output, etc., allowing the Switch to switch freely between the handheld and the host. This is why the new MacBook and MacBook Pro only use the Thunderbolt 3 interface (the appearance is the same as USB-C, and the function is compatible with USB 3.1).
USB-C supports the USB Power Delivery charging protocol (referred to as the PD charging protocol), which enables breakthroughs in the input current and voltage of mobile phone charging, up to “20V 5A”.
In addition, the three new iPhones released in 2017 also support the PD charging protocol, using a “high-voltage and low-current” fast charging solution, with an input power of up to 15W, but the power will be reduced to about 7.5W after the battery reaches 75%.

Tips: How to make mobile phone charging faster?
After clarifying the principle and type of fast charging of mobile phones, the ways to improve the charging speed of mobile phones are clear at a glance:
1.Reduce playing phone while charging
2.Turn on “power saving mode” to charge
3.Choose a suitable fast charge charger
The first two points are well understood and belong to the skills that can slightly increase the charging speed.
For mobile phones that use the “high-voltage and low-current” fast charging solution, due to the step-down process inside the mobile phone, heat loss will occur, so fast charging is usually not activated when the screen is on to prevent the body from overheating.

When the “power saving mode” (called “low battery mode” in iOS) is turned on, the power consumption of the mobile phone system will be reduced, so the charging speed will be faster. At present, Fast Charging and other apps that claim to be able to make the charging speed faster also use a similar principle-to improve the charging speed of the mobile phone by strictly controlling the power consumption of the mobile phone.
In fact, choosing a suitable charger may seem trivial, but it is the part that most affects the charging efficiency of a mobile phone.
For Android
For Android phones that support fast charging, the original charger usually has the fastest charging speed (but there are counterexamples, Huawei P9 does not have a standard fast charging head).
For example, if Huawei Mate 10 uses the standard HUAWEI SuperCharge charger, it can be charged with a low voltage and high current of “5V 4A”, but if other chargers are used, the fast charging effect cannot be guaranteed.
If you are not sure whether your charger supports fast charging, you can also simply judge by the parameters marked on the charging head:
The “Circle Lightning” logo indicates that it supports Qualcomm’s Quick Charge technology. As long as your phone is equipped with a Qualcomm processor, you can basically use this charging head to achieve fast charging.
“Output power” determines the speed of charging, charging heads with a power above 15W are all fast charging heads. Generally speaking, the charging speed of the charging head with higher power will be relatively faster, but it depends on the support of the model.
It is worth mentioning that the power of mobile phone charging is controlled by the mobile phone, and there is a “handshake protocol” between different standards. The charger will automatically adjust the input power according to the instructions of the mobile phone, so there is no need to worry about the high-power charger burning the mobile phone. On the contrary, high-power chargers are not easy to run at full load, so the heat generation will be smaller than that of low-power chargers.
For iOS
As for the standard 5W iPhone, if you want fast charging, you can also consider buying a 12W charger, which is also a cost-effective fast charging solution for iOS devices.
The 12W charger can also charge the old iPhone 6s and iPhone 7, and can achieve a maximum charging power of 10W, which is also much faster than the 5W charger.
Now the new 18w and 20w type-c chargers charge iPhone11 and iPhone12, and can charge iPhoneX, 11 and iPhone12. The user experience has been significantly improved.

Fast charging is also a manifestation of human technological progress Before fast charging, many people, including me, had the habit of sleeping and charging at night. But now as long as you get up and plug in the charger, you will have enough power before you go out early after eating. And if you are on a business trip and office, as long as you have time to charge for more than ten or twenty minutes, it can support your work needs for a day. Before the battery capacity has no breakthrough technological changes, it is a very good experience to buy a fast charge to increase the charging speed. No longer have to worry about the small remaining battery when you go out.
